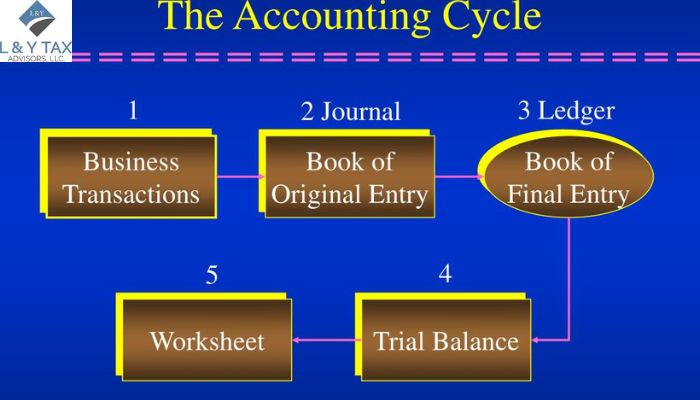
What is the 5 Step Accounting Cycle?
Have you wondered what is the 5 step accounting cycle? Well, who knew you’d be able to manage your business’ monies in a cyclic manner!
The five-step accounting cycle is an essential procedure for guaranteeing the correct documentation and reporting of your company’s financial activities.
To ensure financial integrity and accurately prepare financial statements, this methodical process is mandatory. Please keep reading to explore each phase of the accounting cycle and its importance.
Step 1: Identify and Analyze Transactions
Recognizing and evaluating every financial transaction is the first stage of the accounting process. To guarantee that every transaction is recorded, review source documents such as:
- Contracts
- Bank accounts
- Invoices
- Receipts
Recognize the type of transaction, whether it is a sale, buy, payment, or receipt. You will learn how it affects the financial accounts. Accurate identification and analysis will make this easier.
Step 2: Record Transactions in the Journal
Accurate transaction journaling is necessary to have trustworthy financial records. Transactions must be entered into the journal when recognized and examined—this process of journalizing. Double-entry accounting sequentially records transactions, with each entry consisting of a debit and a credit.
By doing this, the accounting formula is kept in balance – the formula is:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Step 3: Post Transactions to the Ledger
Posting the transactions to the general ledger comes next after journalizing. A group of accounts called the ‘ledger’ is used to organize and compile journal entries for each transaction.
The posting process entails moving the credit and debit amounts from journal entries to the corresponding ledger accounts. This phase facilitates transaction organization and offers a clear picture of each account’s balance.
Step 4: Prepare an Unadjusted Trial Balance
A trial balance, a crucial tool in accounting, is generated after every transaction has been posted to the ledger. It presents all the ledger accounts and their current amounts as of that particular day, providing a snapshot of the financial status.
To validate the accuracy of the ledger entries, the trial balance checks that total debits and total credits are equal. Errors must be corrected before proceeding if there are any variances.
Step 5: Make Adjusting Entries and Prepare Financial Statements
The final step is to adjust entries to reflect accumulated and deferred items. It guarantees that all expenses and revenues are documented within the relevant accounting timeframe.
Posting and journaling adjustments are made to the ledger. Once modifications are made, an updated trial balance is created. This adjusted trial balance is used to create financial statements. These records give a thorough picture of your company’s financial situation, including:
- Income statement
- Balance sheet
- Cash flow statement
The 5 step of accounting cycle is a systematic process essential for maintaining accurate financial records. It begins with analyzing transactions and identifying and recording economic activities like sales and expenses. Next, journal entries document these transactions chronologically. These entries are then posted to the ledger, summarising each account’s balances. The trial balance step follows, where debits and credits are checked for accuracy. Finally, financial statements are prepared, clearly showing the company’s financial performance and position. Understanding these 5 steps of accounting cycle is vital for accurate and reliable financial reporting.
The Bottom Line
So, now you’ve mastered what is the 5 step accounting cycle!
This cycle helps keep correct records and generate trustworthy financial accounts. It will also help you make decisions. Carefully following these processes guarantees compliance with your accounting standards and financial correctness.
Click here to get our QuickBooks & Bookkeeping services.


